Welcome to the ultimate guide on caring for your bearded dragon, where we provide expert tips and advice to ensure your scaly friend’s well-being. From baby beardies to adult bearded dragons, we cover all the essentials.
Discover the importance of warm water baths, proper hydration with fresh water and water bowls, the significance of ultraviolet light, and the benefits of using a spray bottle. Learn about nutritious food options like Dubia roaches, mustard greens, and collard greens, and the role sources of heat like heat lamps and heat dishes.
Get ready to become a bearded dragon care pro!
Ultimate Guide to Caring for Bearded Dragon

Bearded dragons are fascinating reptiles known for their friendly demeanor and unique appearance. These amazing creatures have spiked skin and a “beard” around their throat, making them popular pets among reptile enthusiasts.
As an owner, understanding their specific needs and providing proper care is essential for ensuring a long, healthy life for your bearded dragon.
In order to create a comfortable environment, it’s crucial to maintain appropriate temperature gradients for your bearded dragon. Providing a warm basking area between 95 to 100°F for babies, and 90 to 95°F for adults is necessary for their overall wellbeing.
Alongside proper heating, monitoring humidity levels, diet, and tank setup plays an important role in the ultimate care guide for these unique pets.
Being responsible for a bearded dragon’s health involves regular check-ups and trips to the vet to ensure they’re thriving in their environment. Keeping an eye on their behavior, such as basking habits and appetite, is a great way to monitor their health.
By dedicating time and effort to understanding their individual needs, you’re setting your bearded dragon up for a fulfilling and contented life.
Choosing Your Bearded Dragon
Species and Breeders
When selecting a bearded dragon, it’s essential to understand the different species available. The Central Bearded Dragon (Pogona vitticeps) is the most common species for pets.
Other species include the Rankin’s Dragon (Pogona henrylawsoni) and the Eastern Bearded Dragon (Pogona barbata). Each species may have slightly different care requirements, so researching the species you’re interested in is crucial.
When it comes to breeders, it is important to choose a reputable and responsible one who prioritizes the health and well-being of the bearded dragons. Check for reviews and ask for references from previous customers.
You can also consider adopting a bearded dragon from reptile rescues, as they often have a variety of species and ages available for adoption.
Costs and Availability
Bearded dragons can be found at pet stores, classified ads, or directly from breeders. When purchasing from a pet store, ensure the store knows about bearded dragon care and sources their animals from reputable breeders.
The initial cost of purchasing a bearded dragon can vary depending on factors such as species, size, age, and color morph. Prices can range from $30 to over $300. It’s important to factor in the ongoing costs of maintaining a bearded dragon, including housing, lighting, heating, and food expenses.
A proper setup can cost between $200 to $600, and ongoing care costs can be around $30 to $50 per month.
When determining the best place to find a bearded dragon, consider the following:
- Breeders: These professionals specialize in breeding bearded dragons, offering a wide variety of species, morphs, and ages. They generally have more in-depth knowledge about their animals’ care.
- Pet Stores: Convenient and easily accessible, pet stores offer bearded dragons at varying ages and prices. However, the staff may not be as knowledgeable about specific care requirements.
- Classified Ads: Online and print classified ads can be an excellent source of local breeders or individuals looking to rehome their bearded dragons. Proceed with caution to maintain the dragon’s health and proper care.
- Reptile Rescues: Adopting a bearded dragon from a reptile rescue can be a rewarding experience, as you provide a home to an animal in need. Be prepared for potential additional care requirements, depending on the bearded dragon’s background.
With proper research and thorough consideration, you’ll be able to find the perfect bearded dragon to bring into your home.
Setting Up a Bearded Dragon Habitat

Terrarium Size and Type
When setting up a habitat for your bearded dragon, choosing the correct size tank according to their age is essential. For instance, babies require a 20-gallon tank measuring 30″ x 12″ x 12″, while juveniles need a 40-gallon tank that is 36″ x 18″ x 16″ in size. Adults should have a 125-gallon tank with 48″ x 24″ x 24″ dimensions.
Remember, length and width are more crucial than height since bearded dragons usually aren’t avid climbers.
Substrate Options
Several substrate options are available, but choosing one that is safe and comfortable for your bearded dragon is crucial. Some popular options include:
- Sand: Fine, dust-free sand, can be used but may cause impaction if ingested.
- Tile: A low-maintenance, easy-to-clean option that helps trim the dragon’s nails.
- Reptile carpet: It is a soft, comfortable choice but must be cleaned frequently to prevent bacterial growth.
Heating, Lighting, and Temperature Control
Proper heating and lighting are essential for bearded dragons; they need UVB rays and adequate heat to thrive. Their basking lamp should be on for about 12 to 14 hours per day, and the basking spot should be between 95 and 100 degrees Fahrenheit.
A thermometer should be used to monitor the temperature within the terrarium.
UVB lighting is vital, as it helps bearded dragons synthesize vitamin D3, which is necessary for calcium absorption. Avoid using compact fluorescent bulbs, as they may not provide adequate UVB radiation. Instead, opt for a tube-style UVB bulb that covers the entire length of the terrarium.
Accessories and Climbing Options
Bearded dragons enjoy exploring and climbing in their habitat, so it’s imperative to provide a variety of accessories to keep them stimulated. Some options include:
- Rocks: Arrange rocks to create basking spots in the terrarium. Natural, flat rocks are preferable and should be securely placed to prevent accidental collapses.
- Branches: Bearded dragons enjoy climbing on branches, especially those from native Australian plants. Avoid using pine or other resinous woods, as they may be toxic to reptiles.
- Hideaways: Providing hideaways within the terrarium can give your bearded dragon security and privacy. These can be created using rocks, logs, or commercially available reptile hides.
Bearded Dragon Diet and Nutrition
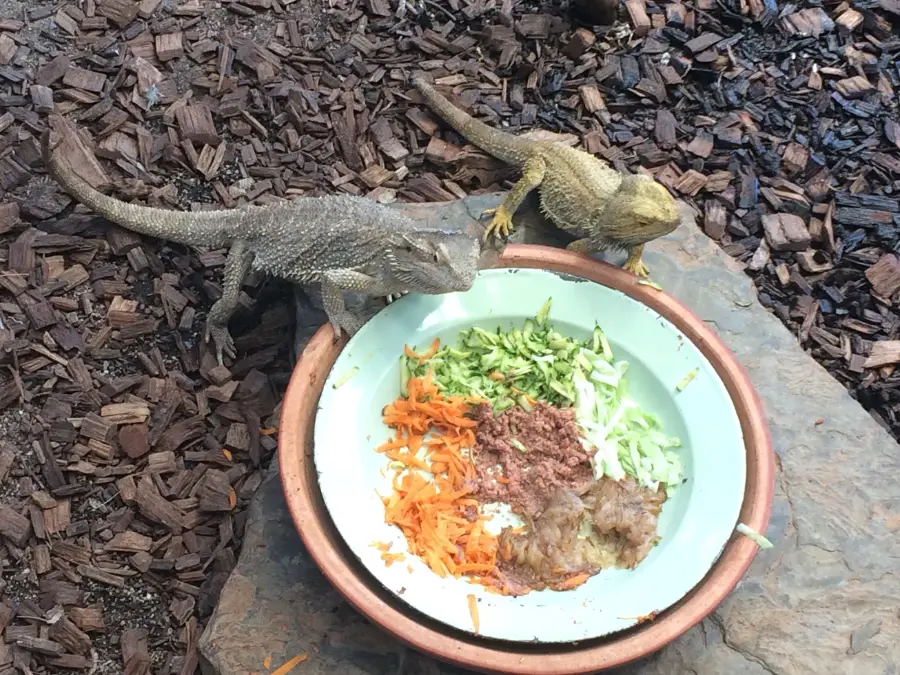

The Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential for the health and well-being of your bearded dragon. As omnivores, they require a combination of insects, vegetables, and fruit to meet their nutritional needs.
Their diet varies based on their age, with younger dragons consuming more insects, around 80%, and 20% vegetables, while adults will eat around 50% insects and 50% vegetables and fruit.
Feeding Insects and Protein Sources
Insects are a critical source of protein for bearded dragons. Common insects fed to them include:
- Crickets
- Mealworms
- Superworms
Remember that the insect’s size should not be larger than the space between the dragon’s eyes. In addition to insects, occasional small rodents or lizards can also be offered as part of their protein intake.
Vegetables and Fruit
Vegetables and fruit should make up a significant portion of a bearded dragon’s diet. They can be offered a variety of options, avoiding citrus fruits, including:
- Leafy greens: collard, mustard, and dandelion greens
- Vegetables: bell peppers, carrots, and green beans
- Fruits: apples, berries, and mangoes
Chop and combine these items into a salad, offering fresh portions to your bearded dragon daily.
Vitamins and Supplements
To ensure proper growth and prevent health issues, bearded dragons require additional vitamins and minerals, including:
- Calcium: Dust food items with calcium powder 3-4 times a week for juveniles, and 1-2 times a week for adults
- Multivitamins: Provide a multivitamin supplement once a week for juveniles, and every two weeks for adults
Monitoring dietary intake and supplementing with vitamins and minerals when necessary can help your bearded dragon maintain optimal health throughout its life.
Bearded Dragon Behavior and Socialization

Temperament and Handling
Bearded dragons are generally docile and easy to handle, making them popular pets. They can adapt well to human interactions, but handling them with care is essential, especially when they are young.
Regular handling will help them become more comfortable with their caregivers. When picking up a bearded dragon, support its body, and avoid grabbing it by the tail as it might cause stress and injury.
Mood and Appearance Indicators
Bearded dragons can exhibit various behaviors that indicate their mood:
- Arm Waving: A bearded dragon may wave its arm to show submission or acknowledge other bearded dragons’ presence.
- Head Bobbing: Head bobbing can signify dominance, particularly in males, during mating or territorial disputes.
- Glass Surfing: Glass surfing occurs when a bearded dragon tries to climb the walls of its enclosure. This behavior may indicate stress, reflection confusion, or inadequate habitat setup.
- Changing Colors: A bearded dragon may change its skin color to regulate body temperature or communicate its mood. Darker colors often indicate stress, discomfort, or the need to warm up.
Mating and Breeding
Mating typically occurs during the spring and summer months, triggered by warmer temperatures and increased daylight hours. Males will display head-bobbing and chase the female during courtship.
Keeping a close eye on the pair is essential to prevent stress or aggressive behavior. Females can lay multiple clutches of eggs after a single mating, so ensure they have a suitable nesting area in their enclosure.
Territorial Behavior and Co-Housing
While some bearded dragons may tolerate co-housing, they can display territorial behavior, especially adult males. It’s best to keep bearded dragons separate to avoid aggression and stress, which may lead to injuries and health issues.
If co-housing is necessary, ensure the enclosure is large enough to provide ample space for each dragon and monitor their behavior closely.
Health Issues and Prevention

Common Health Problems
Bearded dragons may face various health issues throughout their lives. Some common problems include:
- Parasites: Internal parasites can cause diarrhea, weight loss, and lethargy.
- Dehydration: Insufficient water intake can lead to issues such as kidney disease and constipation.
- Respiratory infections: High humidity or poor ventilation can result in respiratory issues.
- Impaction: Consuming non-digestible items or not having proper substrate can cause blockage in the digestive system.
Shedding and Skin Health
Shedding is a natural process for bearded dragons, which can occur multiple times per year. To maintain skin health, ensure proper humidity levels within the tank. If shedding issues arise, consider providing a shallow water dish for them to soak in. Furthermore, never force peeling shed as it may cause harm.
Maintaining Proper Hygiene and Cleaning
Keeping a clean tank is crucial for bearded dragon health. Follow these guidelines to maintain proper cleanliness:
- Spot clean daily: Remove feces, uneaten food, and soiled substrate.
- Change substrate: Replace your dragon’s substrate every few weeks or as needed.
- Monthly cleaning: Disinfect the tank and its contents at least once a month.
Proper hygiene also extends to regular bathing. Bathe your bearded dragon every 10 to 30 minutes in lukewarm water, avoiding detergents or soaps. If your bearded dragon defecates during the bath, rinse them off immediately.
Veterinary Care and Checkups
Regular veterinary checkups are essential for a healthy bearded dragon. Aim for at least annual visits, or more frequently if health problems arise. Immediate veterinary attention is necessary if your dragon appears to be suffering from any health issues mentioned earlier. Building a relationship with a qualified reptile veterinarian enhances your bearded dragon’s chance of receiving proper care and having a long, healthy life.
Bearded Dragon Care Guide – Watch this Beginners Guide
Special Bearded Dragon Care Considerations
Brumation and Hibernation
Brumation is a period of dormancy that bearded dragons undergo, similar to hibernation in mammals. During brumation, your bearded dragon may become less active, eat less, and possibly spend more time buried under bedding or in a hiding spot. It can last several weeks to months and usually occurs when temperatures drop or days become shorter. To provide proper care during brumation, ensure your dragon has adequate hiding spots and maintain proper temperature gradients in the enclosure.
Understanding Bearded Dragon Moods and Cues
To keep your bearded dragon happy and healthy, it’s essential to understand their moods and cues. Here are some common behaviors and what they might mean:
- Alert and active: If your dragon is bright-eyed, active, and seems interested in their surroundings, they are likely in good health.
- Arm-waving: This behavior may signify the submission or acknowledgment of another animal.
- Head-bobbing: Generally a sign of dominance or courtship, especially in males.
- Mouth gaping: Gaping can be a normal way for your dragon to regulate their body temperature.
Be sure to monitor your dragon’s behavior and address any concerns, especially if they exhibit signs of stress or discomfort.
Preventing Impaction and Metabolic Bone Disease
Impaction is a serious condition resulting from the ingestion of indigestible materials. To prevent impaction, choose appropriate flooring for your dragon and remove any small objects that could be accidentally ingested.
Metabolic bone disease (MBD) is a common health issue in captive reptiles caused by improper nutrition or insufficient UVB exposure. To prevent MBD, provide a proper diet including calcium supplements, and make sure your dragon has access to a UVB light source.
Feeding and Hygiene
It’s important to avoid cross-contamination when feeding your bearded dragon. Use separate bowls and dishes for insects, vegetables, and water. Clean their enclosure regularly, including bathing spots and hiding areas, to maintain proper hygiene and reduce the risk of bacterial infections.
In addition to cleaning the enclosure, bathing your bearded dragon regularly can help with shedding and hydration. Allow your dragon to swim for 10-30 minutes in a shallow container, taking care not to use soaps or detergents. If your dragon poops in the water, rinse them off immediately.
Conclusion: Caring for Your Bearded Dragon

Caring for your bearded dragon involves a comprehensive understanding of its habitat, diet, and suitable temperature ranges. You must ensure your pet thrives by maintaining the appropriate basking area temperatures and providing UVB rays through their basking lamp for 12-14 hours per day.
Implementing a balanced diet is crucial to your bearded dragon’s health. This consists of a mix of protein and plant matter in varying proportions depending on their age. Younger dragons need more protein, while adults require more vegetables and fruits.
When it comes to feeding frequency, it’s essential to offer 10 to 15-minute feeding sessions. For example, bearded dragons can eat up to 60 crickets per day, and removing any uneaten insects from their habitat is crucial.
Bathing your bearded dragon can provide a variety of benefits, such as helping with hydration, shedding, and cleanliness. Keeping the bathing water at the correct temperature is vital and monitoring your pet’s comfort during their swim is vital.
By following this guide, you’ll be prepared to provide the proper care for your bearded dragon, contributing to its overall health, happiness, and longevity. As a responsible pet owner, stay up-to-date on the latest bearded dragon care practices and continually monitor your pet’s well-being to ensure they live a fulfilling life.
