Discover the enchanting world of the Leucistic Sugar Glider, a truly extraordinary pet experience. Unlike the familiar Standard Grey or Melanistic Gliders, Leucistic Gliders possess a mesmerizing appearance due to their recessive trait. With their distinctive white collar, black knuckles, and uniquely white hands, these Gliders are a sight to behold.
Dive into the fascinating genetics of the Platinum Genes that create this captivating creature. Welcome to a pet ownership journey like no other!
Leucistic Sugar Glider: Everything You Need to Know
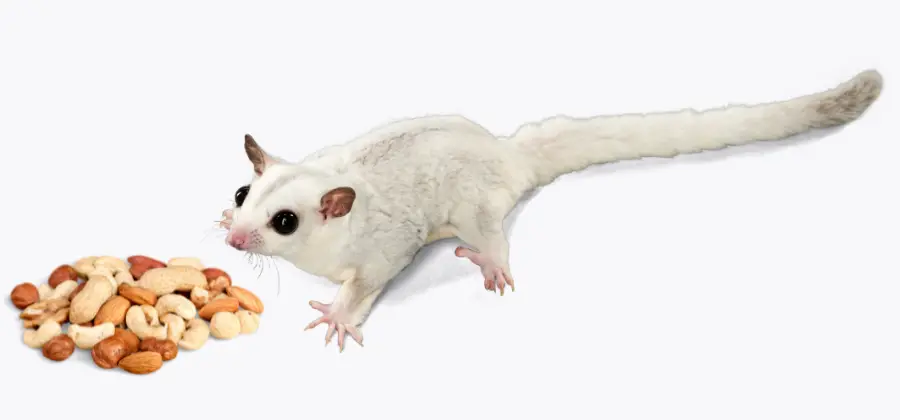

Sugar gliders are unique marsupials native to regions spanning from Australia to Indonesia. Their natural habitats are often tree-dense forests, and their gliding abilities help them navigate the environment. As for their lifespan, it generally ranges from 3 to 9 years in the wild, with some individuals living longer in captivity.
Leucistic sugar gliders are a fascinating variation of the popular and adorable sugar glider species. These unique creatures sport an all-white coat, giving them a striking and distinctive appearance.
Their black eyes, combined with their white fur, have earned them the nickname “black-eyed whites.” Some may even display faint yellowish markings in areas where standard gray gliders usually have their markings.
Native to Australia, sugar gliders are small, omnivorous, and arboreal mammals known for their ability to glide through the air. They have a strong preference for sugary foods like sap and nectar, hence their name. Though they resemble flying squirrels, they are not actually closely related to them, representing an interesting example of convergent evolution.
Considering their unique look and active, social personalities, leucistic sugar gliders, like regular sugar gliders, make intriguing pets when cared for properly. Before adopting one, it’s essential to understand their specific needs and behaviors. So, with your interest piqued, let’s dive into the world of the captivating leucistic sugar gliders!
Leucistic Sugar Glider Vs. Albino
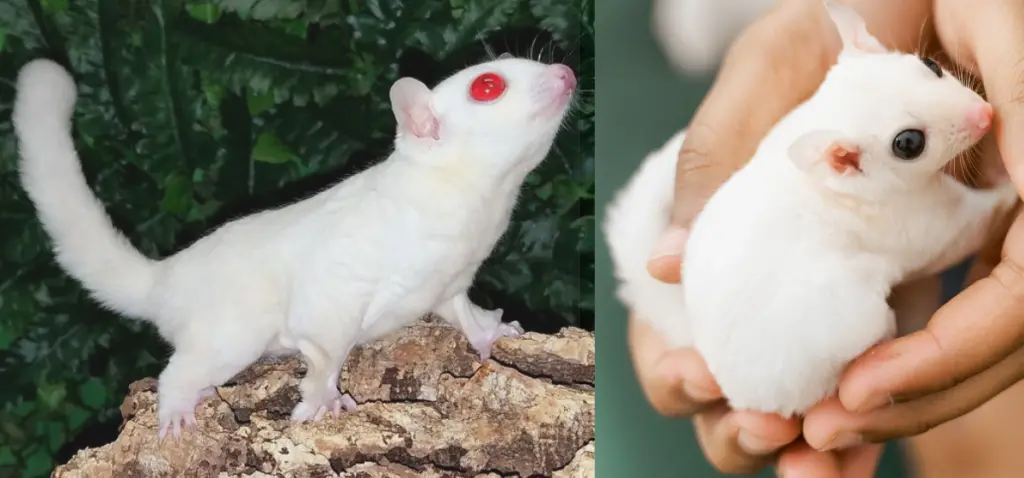
Differences Between Leucistic and Albino Sugar Gliders
Leucistic sugar gliders are characterized by their all-white fur and black eyes. They may also have faint yellowish markings in areas where standard gray gliders would have them. These gliders are sometimes referred to as “black-eyed whites” due to their unique appearance.
In contrast, albino gliders have all-white fur but red eyes, a common trait among albino animals of various species.
Another distinction between the two lies in their sensitivity to light. Leucistic sugar gliders may experience sensitivity to light due to their pigment deficiency, affecting the tyrosinase enzyme responsible for melanin production.
On the other hand, albino gliders do not have any melanin pigmentation in their eyes, skin, and hair, which can result in increased sensitivity to sunlight.
Genetic Background
Leucistic and albino sugar gliders both possess recessive genes that determine their unique coloration. The recessive nature of these genes means that an individual must have two copies of the gene – one from each parent – to exhibit the associated trait.
In the case of leucistic sugar gliders, the genetic mutation affects the production of tyrosinase, an enzyme responsible for melanin production. This results in the white fur, black eyes, and, sometimes, pink or red eye coloration seen in these animals.
For albino sugar gliders, the genetic inheritance comes from recessive alleles that lead to a lack of melanin pigmentation. This is manifested in the characteristic red eyes and white fur. To produce an albino offspring, both parents must carry the albino gene, even if they are not albino themselves.
In summary, leucistic and albino sugar gliders differ in their eye color and genetic background. While they both possess recessive genes affecting their pigmentation, the specific mutations lead to distinct features in their appearance and sensitivity to light.
Color Variations and Patterns

Sugar gliders come in a wide variety of colors and patterns. In this section, we will discuss some of the most common color variations, including Classic Gray, Platinum, and Caramel sugar gliders.
Classic Gray
The Classic Gray sugar glider is the most common color variation found in these exotic pets. Their fur is predominantly gray with a black stripe running down their spine, white underbelly, and black-tipped tail.
Sometimes, they may have lighter gray patches or even small white spots on their body. These gliders have a striking appearance and make wonderful pets for those who admire their unique color pattern.
Platinum
Platinum sugar gliders are a stunning color variation that is much rarer compared to Classic Gray. These gliders have a beautiful, light silver-gray coat with a faint black stripe running down their spine. Their underbelly is often a creamy white color, giving them an elegant and sophisticated appearance.
Interestingly, Platinum sugar gliders can also come in a Ruby Platinum variation, which combines the stunning platinum color with red eyes. This unique combination is the result of two recessive color genes coming together, making Ruby Platinum sugar gliders even more elusive and prized among enthusiasts.
Caramel
Caramel sugar gliders are another beautiful color variation that features a warm, golden-brown coat instead of the traditional gray. Their fur pattern remains similar to the Classic Gray, with a black stripe running down the spine and a white underbelly. However, their coat takes on a lovely cinnamon-like shade, making them visually striking and highly sought after.
Though, it’s essential to note that sometimes, a Cinnamon Sugar glider may appear as Caramel due to a bad diet leading to fur discoloration. So, it’s crucial always to provide a proper diet for these adorable creatures to maintain their true colors and overall health.
In conclusion, sugar gliders exhibit a vast array of colors and patterns, making them a perfect fit for anyone looking to add a unique and charming pet to their family. It is essential to remember that no matter the color or pattern, these animals require proper care, a balanced diet, and ample attention to thrive, so always ensure to dedicate time and resources to their well-being.
Unique Physical Features
Leucistic sugar gliders exhibit some distinctive physical features that set them apart from their standard gray counterparts. In this section, we’ll explore their unique eye coloration and fur patterns.
Eye Coloration
Unlike albino sugar gliders that have red eyes, leucistic sugar gliders possess black eyes. This striking contrast between their eyes and ultra-white fur instantly captures attention and makes them easily distinguishable from other sugar glider color morphs.
Fur Patterns
Their fur is entirely white or sometimes may have faint yellowish markings in the areas where standard gray gliders would have markings. This lightening of their fur color is due to a lack of melanin, which is the pigment responsible for coloring fur and skin in animals.
The leucistic sugar glider’s rounded face and overall appearance make them a charming and exotic choice for pet owners. However, it’s crucial to remember that these fascinating creatures require the same level of care, attention, and commitment as any other sugar glider breed.
With their black eyes and contrasting white fur, leucistic sugar gliders are captivating animals that delight owners and admirers alike. While their fur discoloration may make them appear more visually striking, it’s essential to approach their care and attention with the same dedication one would provide for any other sugar glider breed.
Breeding and Genetics
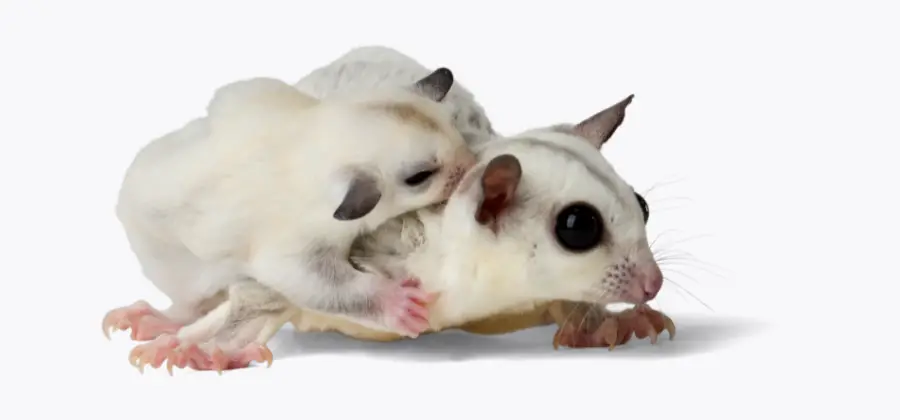

Inheritance Patterns
When breeding sugar gliders, it’s important to understand the genetics and family background of the pets involved. Leucistic sugar gliders are all white with black eyes and may have faint yellowish markings where the black would be on standard gray coloration. The leucistic gene is recessive, following the principles of Mendelian genetics.
In order to produce a leucistic offspring, both parent sugar gliders must carry the leucistic gene. This means that a sugar glider with a white tip tail is likely a recessive or normal trait. When two sugar gliders carrying the leucistic gene breed, they can produce white offspring, which will be homozygous recessive.
Responsible Breeding Practices
To prevent inbreeding, it’s crucial to ensure that sugar gliders are genetically compatible before housing them together for breeding. This information can be obtained through pedigree programs offered by various organizations, such as The Pet Glider LLC. The idea is to avoid breeding pairs that are too closely related.
Some important breeding guidelines to follow:
- Do not breed albino sugar gliders with each other. An ideal pairing would be albino to het or het to het.
- Breeding pairs should be preferably more distantly related to reducing the risk of passing on genetic issues to their offspring.
By following responsible breeding practices, sugar glider breeders can produce healthy and genetically diverse pets for families to enjoy.
Mosaic Sugar Glider Varieties
Watch this Mosaic Sugar Glider Showcase: Ernie & Chloe’s Stunning New Joey
White Mosaic Sugar Gliders
White Mosaic Sugar Gliders are one of the most popular variations of the mosaic sugar glider. These gliders have a primarily white fur coloration, with little to no dark fur. They may have dark spots on their ears, which help distinguish them from leucistic sugar gliders.
Their genetics may or may not be related to leu genetics, and they are often mixed up with leucistic sugar gliders due to their similar appearance. White Mosaic Sugar Gliders are easily identifiable as they must be born almost entirely white.
Piebald Sugar Gliders
Piebald Sugar Gliders, another variety of mosaic sugar gliders, exhibit a unique spotted fur pattern. These gliders have patches of white fur interspersed with patches of their base fur color, often standard gray.
The patches can vary in size and shape, resulting in no two piebald gliders having the same pattern. They are different from white mosaic sugar gliders, which have predominantly white fur with almost no dark spots.
Mosaic sugar gliders, in general, encompass many color variations, sometimes even combinations with recessive traits, like monistic (mosaic leucistic), carmino mosaics, and true platinum mosaics. Due to the vast variation in mosaic gliders, their prices can range widely depending on the specific variety and rarity.
Caring for a Leucistic Sugar Glider
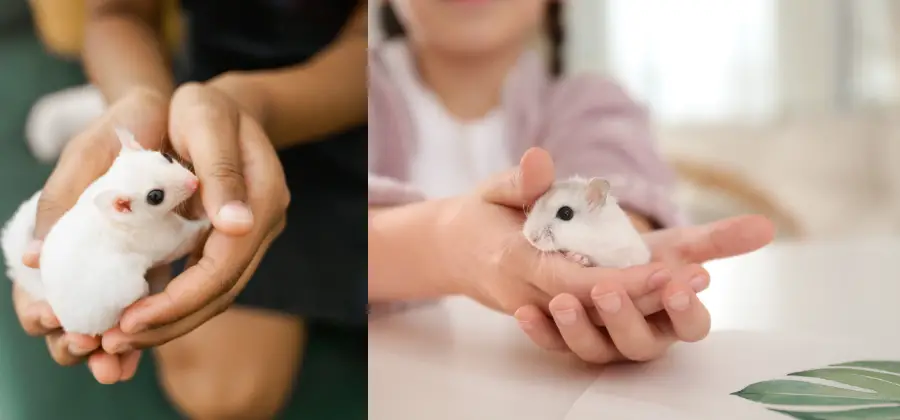

Leucistic sugar gliders, like their counterparts with different color variations, have specific care requirements to ensure they live healthy and happy life. The following sections will discuss their dietary needs, housing, and socializing aspects.
Dietary Requirements
Sugar gliders are omnivorous animals, which means they require a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables, and protein sources. Here are some key aspects of their diet:
- A mix of fruits and vegetables: Offer fresh produce such as apples, grapes, berries, green beans, and carrots.
- Protein sources: Animal-based proteins like cooked chicken or turkey and insect-based proteins like mealworms and crickets.
- Supplements: Occasionally, include calcium supplements and multivitamins to ensure they get enough nutrients in their diet.
It is crucial to provide a diverse and balanced diet for your leucistic sugar glider to maintain their overall health and minimize the risks of vitamin deficiencies and other health issues.
Housing
Leucistic sugar gliders require a tall and spacious cage, as they love to climb and jump. Consider the following when setting up their habitat:
- Cage dimensions: At least 24x24x36 inches (LxWxH) to provide ample space for movement and play.
- Accessories: Incorporate several branches, perches, and hiding spots (like nest boxes) to create a stimulating environment.
- Cleanliness: Ensure regular cleaning of the cage, food bowls, and water bottles to maintain a hygienic space for your pet.
- UVB lighting: As these gliders are prone to eye and skin issues due to their lack of pigmentation, provide them with adequate UVB lighting to support their overall health.
Socializing
Sugar gliders are highly social creatures and thrive in groups or with a buddy. Keep these factors in mind to ensure a well-adjusted and happy glider:
- Pair or group them: Ideally, keep at least two sugar gliders together to help them fulfill their social needs.
- Introductions: When introducing a new glider, make sure to do it gradually and supervise their interactions to avoid conflicts.
- Playtime: Regularly engage with your glider outside their cage, allowing them to explore and interact with you in a safe space.
By taking care of your leucistic sugar glider’s dietary requirements, housing, and social needs, you can ensure a healthy and content pet that brings joy to your household.
Sugar Glider Natural Habitat and Lifespan

Sugar gliders are native to Australia, Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea. They thrive in various forest habitats, including eucalyptus forests, and often live in remnant bush patches.
These little marsupials are arboreal, meaning they primarily live in trees. They are well-equipped with their gliding membrane, known as a patagium, enabling them to “fly” from one tree to another. This adaptability helps them access food sources and escape predators.
When it comes to their lifespan, sugar gliders live for around:
- 3 to 9 years in the wild
- Up to 12 years in captivity
- Maximum reported lifespan of 17.8 years
In the wild, their lifespan can vary greatly depending on factors such as diet, predation, and environment. However, leucistic sugar gliders (a specific genetic variation resulting in reduced pigmentation) do not show any significant difference in lifespan compared to their normally pigmented counterparts.
Sugar Glider Diet
Sugar gliders have a diverse diet consisting of:
- Nectar
- Fruits
- Insects
- Vertebrates
Their preference for sweet foods like nectar and honey earned them the name “sugar glider.” They are opportunistic feeders, which means they eat what’s available in their environment. This flexible diet allows them to adapt to various habitats, thereby increasing their chances of survival in the wild.
Conclusion: Leucistic Sugar Glider

Discover the fascinating world of Leucistic Sugar Gliders, a subspecies of Sugar Gliders with a variety of patterns, including the iconic Dorsal Stripe. Their unique color traits make them an ideal candidate for breeding, and their gray markings and mosaic characteristics set them apart. Experience the beauty of the White Glider, driven by its dominant gene.
The Leucistic Sugar Glider offers a unique and mesmerizing pet experience. Whether you’re fascinated by the stunning Albino Gliders, the diverse color patterns, or the intriguing genetics of the Platinum Genes, these gliders are a true wonder.
From the black knuckles and white collar to the distinct white hands and white feet, these pet sugar gliders appearance is simply captivating. With their recessive traits and variety of color types, including Caramel Gliders and Mosaic Gliders, they offer endless patterns and possibilities.
As you consider these extraordinary creatures as potential pets, remember the importance of a balanced diet and proper care to ensure their happiness and well-being. Get ready to embark on a journey with these beautiful and engaging Leucistic Sugar Gliders that will surely bring joy and wonder into your life.

